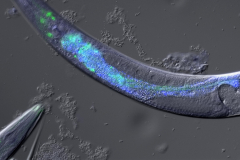
The SnAvi-tag is a novel in-vivo fluorescent tag combining several features to allow for tandem-purification, western blotting and in-vivo subcellular localization of proteins fused to it. It has been shown to work in expression systems as diverse as C. elegans, E. Coli and vertebrate cells. For further information see Schäffer et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan 4: SnAvi–a new tandem tag for high-affinity protein-complex purification (PMID: 20047968)
 latest worm papers
latest worm papers- Adaptive ER stress promotes mitochondrial remodelling and longevity through PERK-dependent MERCS assembly
- Insulin and epidermal signals independently shape sexually dimorphic neurite branching in C. elegans
- Distant Homology BLASTP Searches
- Effects of dry-heating time on the physicochemical properties of abalone myofibrillar protein-polysaccharide conjugates and the antioxidant activity of their in vitro digestion products
- Anticancer bioactive phytochemicals screening from medicinal-edible homologous materials in Caenorhabditis elegans
- Leucine inhibits degradation of outer mitochondrial membrane proteins to adapt mitochondrial respiration
- Nonlinear integration of sensory inputs and behavioral state by a single neuron in C. elegans
- WormSNAP: A software for fast, accurate, and unbiased detection of fluorescent puncta in C. elegans
- Nicotine affects sensory-motor coupling in C. elegans
- Insight into immunoregulatory and neuromodulatory capability of Bacteroides cellulosilyticus and Bacteroides xylanisolvens human gut microbiota isolates
- P-glycoprotein-9-mediated multidrug tolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PCMD-1 stabilizes the PCM scaffold and facilitates centriole separation
- Tardigrade Dsup extends C. elegans life span by impeding mitochondrial respiration and promoting oxidative stress resistance
- A positive feedback loop promotes the active internal state of the C. elegans egg-laying circuit
- Viral RNA pUGylation promotes antiviral immunity in C. elegans
- Parental age selection in C. elegans influences progeny stress resistance capacity
- Bioactive peptides from Spanish dry-cured ham: In vitro and in vivo antioxidant effects using a Caenorhabditis elegans model
- Protective effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide on DNA damage and cell death in A549 cells and aging in C. elegans caused by hydrogen peroxide
- IL-1β alters the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- 20(S)-protopanaxadiol prolongs lifespan and enhances stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans via the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway